Comprehensive Eye Care

What is Comprehensive Eye Care?
Comprehensive eye care goes far beyond simply updating your prescription. It’s a proactive approach to maintaining optimal eye health and detecting potential problems before they threaten your sight.
At Center for Sight, we understand that early detection is essential to preserving vision. Many serious eye conditions develop silently, showing no symptoms until permanent damage has already occurred.
Our comprehensive approach combines advanced diagnostic technology with personalized care to safeguard your vision for years to come.
Common Eye Conditions We Treat
Refractive Errors
Nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism occur when the eye’s shape prevents light from focusing properly on the retina, causing blurred vision. Dr. Newman and our expert team offer a wide selection of glasses and contact lenses to correct your refractive errors and improve your vision.
Floaters & Flashes
Floaters appear as moving spots or cobweb-like shapes caused by age-related changes in the eye’s vitreous gel. While typically harmless, sudden increases accompanied by flashes, peripheral vision loss, or shadow-like curtains require immediate attention as they may indicate retinal detachment.
Macular Degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss in adults over 50, affecting the central portion of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. Dry macular degeneration progresses slowly and accounts for about 90% of AMD cases.
Early symptoms include a gradual loss of central vision, difficulty reading, and a need for brighter lighting. Wet macular degeneration involves the abnormal growth of blood vessels beneath the macula, which can leak fluid and blood, leading to rapid vision loss.
This form requires prompt treatment to prevent severe vision impairment.
Diabetes
Diabetes significantly impacts eye health by damaging the delicate blood vessels throughout the retina. Diabetic retinopathy develops when elevated blood sugar levels weaken these blood vessels, causing them to leak fluid, blood, or both.
Early diabetic retinopathy often produces no symptoms, making regular eye examinations crucial for diabetic patients. As the condition progresses, you may experience blurred vision, fluctuating vision, or dark spots in your visual field.
Diabetes can also accelerate cataract formation and increase the risk of glaucoma. Additionally, diabetic macular edema, a condition characterized by swelling in the central retina, can cause significant vision loss.
Early detection and treatment can often prevent or minimize vision-threatening complications. We also provide diabetic education resources to help patients understand the connection between blood sugar control and eye health.
Crossed, Turned, & Lazy Eye
Strabismus occurs when eye muscles become imbalanced, causing misalignment. This leads to double vision and potentially amblyopia (lazy eye) if the brain ignores the weaker eye’s signals.
These conditions are more common in children but can affect adults after injury or illness.
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as “pink eye,” encompasses several conditions affecting the thin membrane covering the white of the eye and inner eyelids.
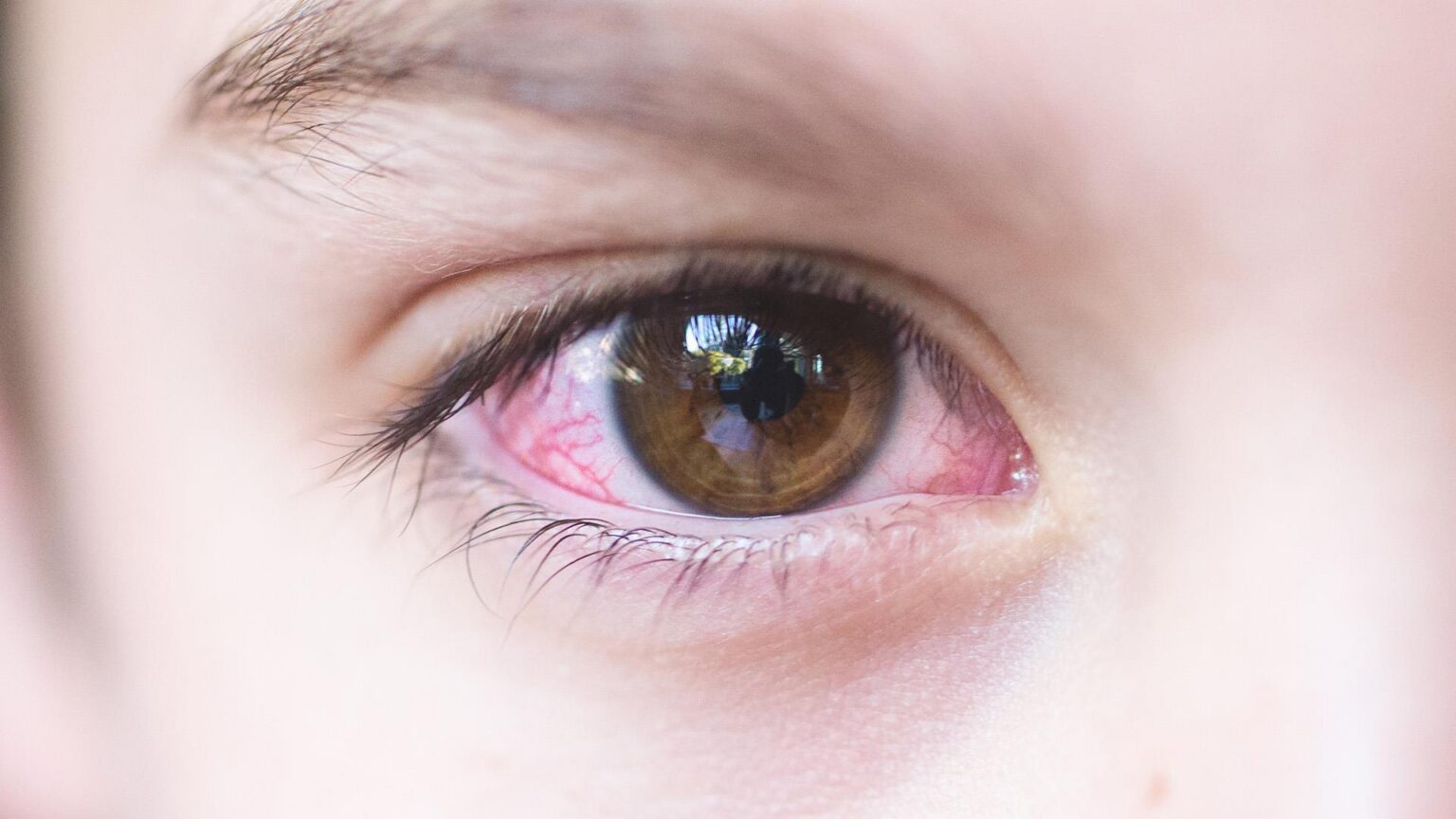
Viral Conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis often accompanies cold symptoms and is highly contagious. Patients typically experience watery discharge, redness, and irritation that worsen between days three and five.
While this form usually resolves on its own, prescription drops may provide comfort and potentially reduce duration.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis produces a thick discharge accompanied by significant redness and discomfort. Various bacteria, including those associated with sexually transmitted infections, can cause this condition.
Treatment requires targeted antibiotic drops or oral medications.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis results from environmental triggers like pollen, pet dander, or dust mites. Symptoms include intense itching, redness, tearing, and sometimes swelling.
Treatment focuses on antihistamine drops, with steroid medications reserved for severe cases.
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis (GPC)
Giant papillary conjunctivitis (GPC) primarily affects contact lens wearers and prosthetic eye patients. Symptoms include contact lens intolerance, itching, heavy discharge, and bumps under the eyelids.
Pterygium
A pterygium is a benign growth of tissue that extends from the conjunctiva onto the cornea, typically appearing as a fleshy, triangular-shaped lesion. Early symptoms include redness, irritation, and a sensation of having something in the eye.
As the pterygium grows, it may cause astigmatism and visual distortion. In advanced cases, it can obstruct vision by covering the central cornea.
Pinguecula
A pinguecula appears as a yellowish or whitish raised area on the conjunctiva. This common condition results from prolonged exposure to sun, wind, and dry conditions.
Most pingueculae cause minimal symptoms, though some patients experience mild irritation, burning, or redness, particularly in dry environments.
Hordeolum
A hordeolum, commonly called a stye, is an acute infection of the oil glands along the eyelid margin. It typically appears as a red, tender bump resembling a pimple, often at the base of an eyelash.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and sometimes a visible pus-filled center. Treatment typically involves applying warm compresses to encourage drainage, although antibiotic ointments may be necessary for persistent or severe cases.
Chalazion
A chalazion forms when an oil gland in the eyelid becomes blocked, creating a firm, painless bump away from the lid margin. Unlike styes, chalazions are typically not infected and cause minimal discomfort.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelids. Symptoms include red, itchy, swollen eyelids with scaling or crusting along the lash line.
Treatment requires consistent eyelid hygiene, including the use of warm compresses and gentle lid scrubs. Severe cases may require topical or oral antibiotics.
Iritis
Iritis is inflammation of the iris, the colored portion of the eye that controls light entering the pupil. This condition can cause significant pain and, if untreated, may lead to serious complications.
Symptoms include severe eye pain, light sensitivity, blurred vision, headache, and redness around the cornea.
Our Optical Services
Whether you need glasses, sunglasses, or contacts, our opticians can help you find quality eyewear that seamlessly integrates into your daily life while providing optimal visual correction:

Glasses
Our comprehensive collection of frames and lenses is designed for every age and lifestyle, including specialized sports eyewear for active individuals, prescription sunglasses, and children’s eyewear. We stay current with the latest lens technologies, offering advanced solutions such as Varilux digital progressive lenses, Transitions adaptive lenses that automatically adjust to changing light conditions, and premium polarized lenses for enhanced visual comfort.
We carefully curate our frame inventory to reflect current fashion trends while maintaining timeless options that never go out of style. Whether you prefer classic sophistication or contemporary bold designs, our collection offers choices that complement your aesthetic.
Our in-house finishing laboratory provides a significant advantage, allowing us to customize and adjust your eyewear quickly and precisely, often while you wait.
Contacts
Contact lenses offer numerous advantages over traditional glasses, including unrestricted peripheral vision, freedom during sports, and the ability to wear non-prescription sunglasses. Many patients with high prescriptions even find that contact lenses provide sharper, more natural vision than glasses.
Center for Sight offers an extensive range of contact lens options to meet virtually any visual need:
We also specialize in fitting contact lenses for unique situations, including therapeutic bandage lenses for corneal healing, specialized lenses for keratoconus, high water content lenses for dry eye patients, and cosmetic color-enhancing or color-changing lenses.




